
Book value is the value of a company’s assets after netting out its liabilities. It approximates the total value shareholders would receive if the company were liquidated. For instance, consider a company’s brand value, which is built through a series of marketing campaigns.
Is BVPS relevant for all types of companies?
It’s a measure of what shareholders would theoretically get if they sold all of the assets of the company and paid off all of its liabilities. Investors can calculate it easily if they have the balance sheet of a company of interest. Investors can compare BVPS to a stock’s market price to get an idea of whether that stock is overvalued or undervalued. Should the company dissolve, the book value per common share indicates the dollar value remaining for common shareholders after all assets are liquidated and all creditors are paid. If a company’s BVPS is higher than its market value per share (the current stock price), the stock may be considered undervalued.
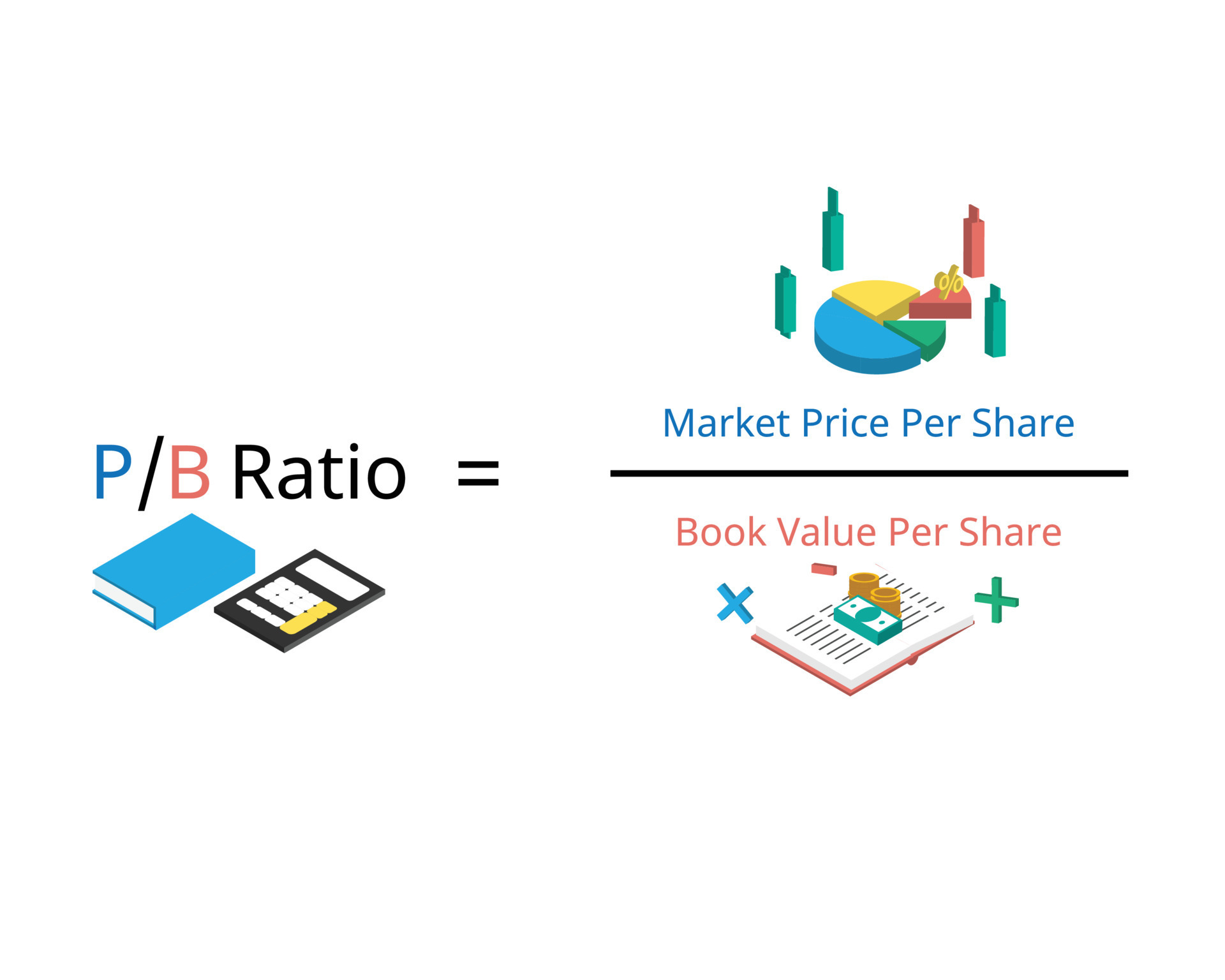
Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio
The book value of equity (BVE) is the value of a company’s assets, as if all its assets were hypothetically liquidated to pay off its liabilities. In Particular, we can review if JPM stock became an exciting opportunity after the stock market crash. It provides services in the area of investment banking, commercial banking, and treasury services, among others. However, during the stock market crash of March 2020, the stock price declined by around 40%. The most significant benefit of our price-to-book ratio calculator is that you can quickly add information and promptly get the historical values for analysis.
How to use the price to book ratio formula
This means that each share of stock would be worth $1 if the company got liquidated. To calculate book value per share, simply divide a company’s total common equity by the number of shares outstanding. For example, if a company has total common equity of $1,000,000 and 1,000,000 shares outstanding, then its book value per share would be $1. The figure that represents book value is the sum of all of the line item amounts in the shareholders’ equity section on a company’s balance sheet. As noted above, another way to calculate book value is to subtract a business’ total liabilities from its total assets. Assume that XYZ Manufacturing has a common equity balance of $10 million and 1 million shares of common stock are outstanding.
- In this article, we will first review what is the book value of equity because that will allow us to understand book value per share and tangible book value per share.
- A company can use a portion of its earnings to buy assets that would increase common equity along with BVPS.
- To put it simply, this calculates a company’s per-share total assets less total liabilities.
- By multiplying the diluted share count of 1.4bn by the corresponding share price for the year, we can calculate the market capitalization for each year.
BVPS is typically calculated quarterly or annually, coinciding with the company’s financial reporting periods. Value investors use BVPS to identify stocks that are trading below their intrinsic value, indicating potential undervaluation. In other words, investors understand the company’s recent performance is underwhelming, but the potential for a long-term turnaround and the rock-bottom price can create a compelling margin of safety. The difference between book value per share and market share price is as follows. In conclusion, the price-to-book value obtained suggests that the market could have undervalued the stock during that time.
Open Your Demat Account in Under 5 Minutes
The term “book value” is derived from accounting lingo, where the accounting journal and ledger are known as a company’s books. Alternatively, another method to increase the BVPS is via share repurchases (i.e. buybacks) from existing shareholders. If relevant, the value of preferred equity claims should also be subtracted from the numerator, the book value of equity.
A company’s stock buybacks decrease the book value and total common share count. Stock repurchases occur at current stock prices, which can result in a significant reduction in a company’s book value per common share. It may not include intangible assets such as patents, intellectual property, brand value, and goodwill. It also may not fully account for workers’ skills, human capital, and future profits and growth.
Enter the Book Value per Share (BVPS), a fundamental financial measure that provides insight into a company’s intrinsic worth. Let’s learn more about Book Value Per Share, its formula calculation and other details. Book your guide to accounting for manufacturing businesses value per share is determined by dividing common shareholders’ equity by total number of outstanding shares. Now, let’s say that Company B has $8 million in stockholders’ equity and 1,000,000 outstanding shares.
